Introduction to Orion Stars
The phrase “Orion Stars” conjures images of celestial beauty, invoking both the mythology of ancient civilizations and modern understandings of astronomy. Orion, one of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky, has fascinated humans for millennia. From ancient stories that wove this constellation into the tapestry of myth, to the cutting-edge technology used to explore the stars in this region, “Orion Stars” captures a spectrum of interest across time, science, and culture.
In this exploration, we will delve deep into the different facets of Orion Stars, ranging from its astronomical significance to its role in ancient mythology and its relevance in modern space exploration.
The Orion Constellation: A Celestial Giant
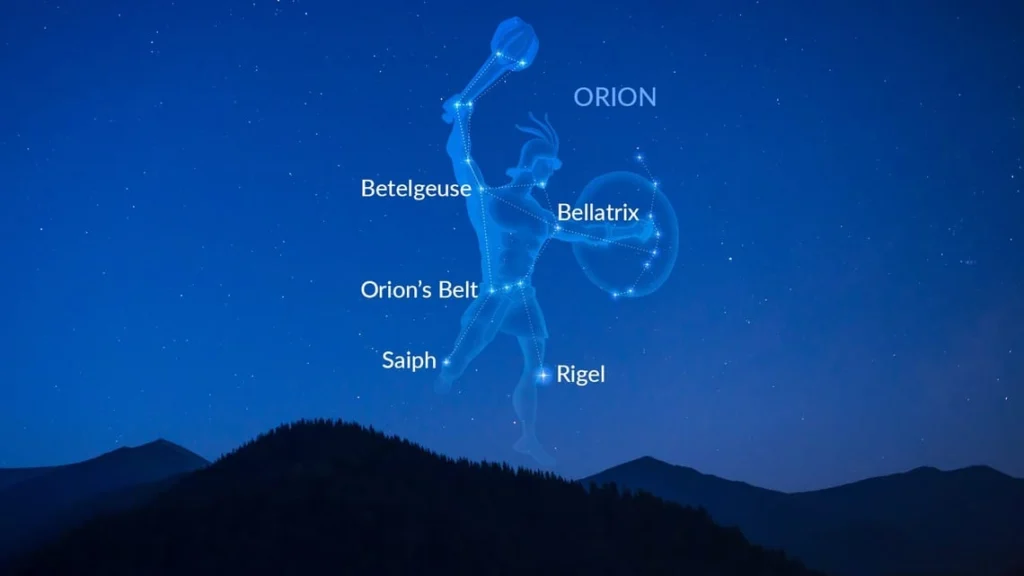
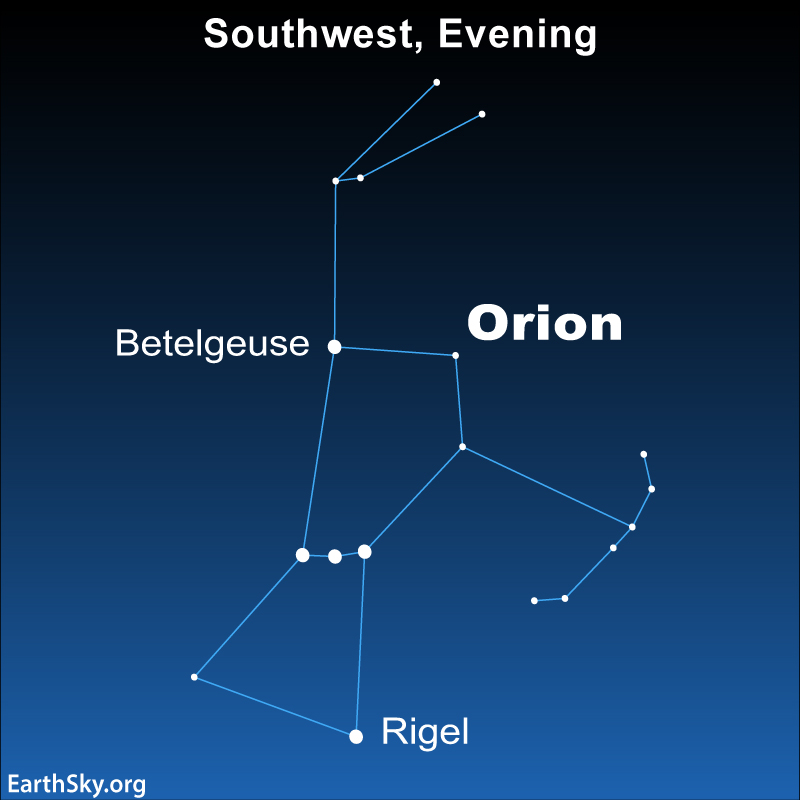
Orion is one of the most visible and iconic constellations in the night sky. Known for its bright stars and distinct shape resembling a hunter, it is located on the celestial equator, making it visible from almost all parts of the world. The constellation consists of several prominent stars, including Betelgeuse, Rigel, and Bellatrix, that form the recognizable pattern of a hunter holding a club and shield.

Orion’s stars are massive, luminous, and relatively young in cosmic terms. These stars are primarily located within the Milky Way, though their brightness makes them stand out against the darker backdrop of space.
Orion in Ancient Mythology
The mythology surrounding the Orion constellation is as captivating as the stars themselves. In Greek mythology, Orion was a mighty hunter, the son of Poseidon, who was placed in the heavens after his death. Different cultures have various interpretations of the constellation. In Egyptian mythology, Orion was associated with Osiris, the god of the afterlife, and was considered a symbol of resurrection.
In Native American cultures, Orion’s belt was often linked to tools or objects essential for survival, symbolizing hunting and the passage of seasons. Similarly, in Chinese astronomy, the stars of Orion were part of a larger group known as the White Tiger of the West, representing autumn.
Key Stars in the Orion Constellation
The Orion constellation comprises several key stars that are bright and massive. Among the most prominent are:
1. Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse, a red supergiant, is one of the most famous stars in Orion. It marks the shoulder of the hunter and is known for its reddish hue. Betelgeuse is nearing the end of its life cycle and is expected to go supernova within the next million years, a short timescale in cosmic terms.
2. Rigel
Rigel is a blue supergiant and the brightest star in the Orion constellation. It represents the hunter’s left foot and emits a striking blue-white light. Rigel is one of the most luminous stars in the night sky and is significantly younger than Betelgeuse.
3. Bellatrix
Bellatrix, marking Orion’s left shoulder, is a hot, blue giant. It is not as bright as Betelgeuse or Rigel but remains a key feature of the constellation.
4. The Belt Stars: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka
Orion’s belt consists of three stars aligned in a straight line: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. These stars are relatively equidistant from Earth and have been used for navigation by various civilizations.
The Orion Nebula: A Stellar Nursery
One of the most spectacular features of the Orion constellation is the Orion Nebula (Messier 42), a massive stellar nursery located in the “sword” of the hunter. The nebula is a vast cloud of gas and dust where new stars are being born. It is visible to the naked eye, making it one of the few nebulae that can be easily observed from Earth.
The Orion Nebula provides astronomers with valuable insights into the formation of stars and planetary systems. The Hubble Space Telescope has captured breathtaking images of the nebula, revealing its intricate structures and the young stars within.
Orion in Astronomy: Modern Significance
Astronomers have long studied the stars of the Orion constellation to understand more about stellar evolution. The variety of stars within the constellation, from young, hot stars to older, dying supergiants, offers a diverse range of study subjects.
One of the most significant astronomical features within Orion is the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, a region filled with young stars, nebulae, and star-forming regions. This area is crucial for understanding how stars form and evolve.
Additionally, the supernova potential of Betelgeuse has captivated scientists. Although it is difficult to predict exactly when Betelgeuse will explode, its relatively close proximity to Earth ensures that when it does, the event will be spectacular, potentially illuminating the night sky for weeks.
Orion in Navigation and Timekeeping
In addition to its beauty and scientific significance, the Orion constellation has played a vital role in navigation and timekeeping throughout history. Mariners and travelers used Orion’s belt as a celestial compass, as it lies nearly along the celestial equator and thus indicates directions.
In ancient Egypt, the rising and setting of Orion were linked to the flooding of the Nile, marking the beginning of the Egyptian calendar year. In various cultures, Orion’s movements in the sky have been associated with seasonal changes, guiding agricultural activities and religious practices.
The Orion Arm of the Milky Way
The Orion stars are part of a larger structure within the Milky Way known as the Orion Arm or Orion Spur. This spiral arm of the galaxy is home to our solar system and numerous star-forming regions, including the Orion Nebula. The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm compared to the larger Perseus and Sagittarius arms, but it contains several prominent star clusters, nebulae, and young stars.
Space Exploration and the Orion Stars
The stars of Orion have captured the attention of not just stargazers but also space explorers. NASA’s Orion spacecraft, designed for deep-space exploration, was named after this constellation, symbolizing humanity’s aspirations to explore beyond Earth. The spacecraft is intended to carry astronauts to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, marking a new era of space exploration.
The connection between the Orion stars and space exploration is fitting, as the stars in this region are some of the most luminous and massive, embodying the spirit of exploration and discovery.
Orion Stars in Popular Culture
Orion’s prominence in the sky has made it a popular cultural symbol, appearing in various forms of media, literature, and art. The constellation has been referenced in works ranging from ancient poetry to modern science fiction. For instance, in the film Men in Black, the phrase “the galaxy is on Orion’s belt” plays a key role in the plot, adding a layer of mystery to the constellation’s cultural significance.
In literature, Orion often symbolizes strength, bravery, and the eternal nature of the stars. The constellation’s unchanging position in the night sky has made it a symbol of constancy and endurance, evoking feelings of awe and wonder in observers throughout history.
Technological Tools for Observing Orion
Advancements in technology have made observing the stars of Orion more accessible to amateur astronomers. High-powered telescopes, long-exposure cameras, and sophisticated software allow stargazers to capture detailed images of the Orion Nebula and its surrounding stars.
Apps and digital platforms provide real-time information on Orion’s position in the sky, helping observers track the constellation’s movement throughout the night and across seasons. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are also being used to simulate the experience of exploring the Orion constellation, bringing the stars closer to people in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago.
Astrological Interpretations of Orion
While Orion’s significance is firmly rooted in astronomy, the constellation also holds importance in astrology. Though it is not part of the zodiac, some modern astrologers associate Orion with strength, determination, and the ability to overcome challenges. Its role as a hunter in mythology has led to interpretations of Orion as a symbol of courage and pursuit of goals.
Astrologers often reference the stars of Orion, particularly Betelgeuse, when discussing influences on personal traits or behaviors, though these interpretations vary widely depending on the astrological tradition being followed.
Future Exploration and Discoveries
As technology continues to advance, the future holds exciting possibilities for the exploration of Orion stars. Astronomers are developing new telescopes and space missions that will allow for more detailed observations of the Orion constellation and the stellar nurseries within it. These discoveries will likely provide deeper insights into the processes of star formation, the life cycles of stars, and the potential for other habitable systems within the Orion region.
The mystery of Betelgeuse’s eventual supernova also looms large in the minds of scientists, who eagerly anticipate the event. When Betelgeuse does go supernova, it will offer a rare and valuable opportunity for astronomers to study the death of a star up close, adding another layer of understanding to the complex phenomena occurring within the Orion constellation.
Conclusion
The Orion stars are more than just points of light in the night sky—they are a gateway to understanding our universe’s past, present, and future. From their role in ancient myths to their significance in modern astronomy and space exploration, the stars of Orion continue to captivate and inspire. As technology advances, the Orion constellation will remain a focus of both amateur stargazing and professional scientific study, offering endless opportunities for discovery and wonder.
Read More: Emoji Kitchen: A Creative Way to Combine and Express Emojis